

In today’s intensely competitive business environment, the importance of customer experience has taken its rightful place that drives or hampers business success in an organization. Consumers and their buying behavior become wiser and aware of their choices; organizations, therefore, must learn that the days of monopoly through making better products and charging reasonable prices are gone. Organizations have changed to make every interaction with customers worthwhile and memorable with the help of an advertising agency in Bangalore.
It needs to be noted that the business success customer focus has radically changed with the advent of the digital era. Today’s customers want omnichannel communication, individual approach, and immediate relevance. Any organization that lacks the capacity to improve customer experience potentiality stands to lose not only single transactions but also patronage relationships. According to a study by the Aberdeen Group, a large number of buyers, 86% to be exact, are actually willing to spend extra for a better experience, making it a critical factor in today’s economy.
Customer Experience (CX) is more than just customer service—it represents the entire perception a customer forms while interacting with a brand across every touchpoint. From the moment a customer first discovers a business, to the point of purchase, and through post-sale support, CX encompasses every stage of the relationship. In today’s competitive landscape, delivering a positive customer experience is no longer optional; it is a differentiator that directly influences loyalty, retention, and advocacy.
Customer Experience (CX) is more than just customer service—it represents the entire perception a customer forms while interacting with a brand across every touchpoint. From the moment a customer first discovers a business, to the point of purchase, and through post-sale support, CX encompasses every stage of the relationship. In today’s competitive landscape, delivering a positive customer experience is no longer optional; it is a differentiator that directly influences loyalty, retention, and advocacy.
The customer journey is rarely linear. Prospects may interact with multiple channels—websites, social media, in-store visits, mobile apps, or call centers—before making a decision. CX is defined by how seamless, consistent, and satisfying these interactions are.
When businesses optimize every stage of this journey, they create memorable experiences that encourage repeat engagement and word-of-mouth referrals.
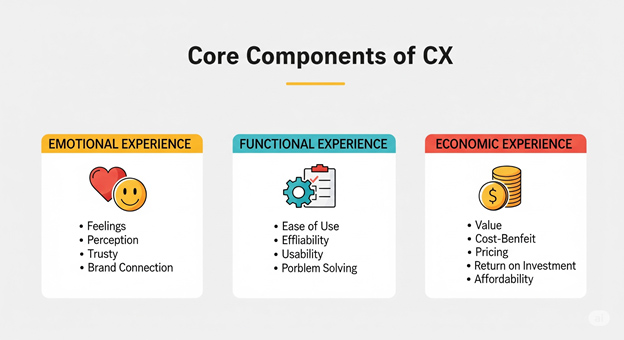
At its core, customer experience can be understood through three key dimensions:
How customers feel during their interactions. Positive emotions like trust, delight, and satisfaction strengthen loyalty. Negative emotions—frustration, confusion, or neglect—drive customers away.
The practical side of CX. This includes ease of use, fast response times, intuitive interfaces, and efficient problem resolution. A product or service may be great, but if processes are complex, customers quickly disengage.
The perceived value customers receive compared to the cost. This isn’t just about low prices—it’s about whether customers feel the product or service justifies their investment in terms of quality, benefits, and long-term value.
When these three components align—evoking positive emotions, ensuring seamless functionality, and delivering strong value— businesses build a customer experience that stands out in crowded markets.
To improve customer experience, organizations need to learn that loyalty is achieved on the basis of more positive incidents. Leads from the first moment when the customer gets to know a specific brand to the times after he makes his purchase decision are responsible for his or her perception of the brand. Common implications arising from a well-executed business success customer focus strategy are that the customer lifetime value will be considerably enhanced. Not only does this approach improve customer experience, but also customer satisfaction turns the users into influencers who recommend the business to others.

Customer experience is a concept that goes well beyond straightforward satisfaction/dissatisfaction numbers. This occurs in many ways to directly affect a company’s bottom line of profit and growth. When there is a creation of excellent service experiences, there will always be more loyal customers, high retention levels, and best of all, references. Research shows that companies that invest in customer experience programs have achieved better top-line growth rates two to four percentage points above those of competitors who do not focus on increasing customer experience.
Delivering exceptional customer experience requires more than good intentions—it demands a deliberate strategy that blends personalization, consistency, and adaptability. Today’s consumers expect brands to know their preferences, anticipate their needs, and provide seamless support across every channel. Businesses that succeed in this area see higher loyalty, stronger word-of-mouth referrals, and long-term growth.
Modern customers interact with brands across a variety of channels—websites, mobile apps, social media, email, chatbots, and in-store touchpoints. A truly exceptional customer experience ensures that each interaction feels personalized and consistent, regardless of the platform.
When businesses master omni-channel personalization and support, they show customers that their time, preferences, and convenience are prioritized—an essential factor in creating loyalty.
Data is the backbone of a powerful customer experience strategy. By capturing insights at every touchpoint, businesses can better understand what customers value, where friction exists, and how expectations evolve.
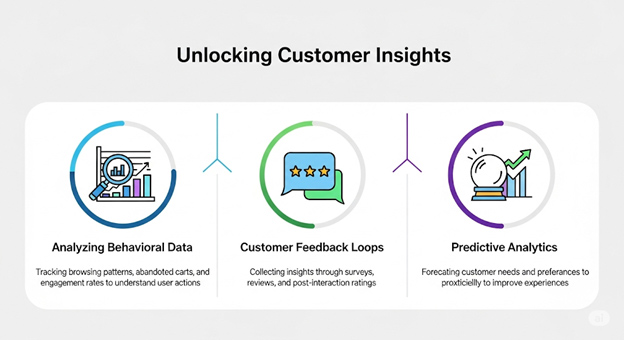
By consistently leveraging data and maintaining open feedback loops, businesses can shift from a reactive approach to a proactive one. This continuous improvement cycle ensures that customer experience is not static, but evolves alongside customer expectations.
Customer experience as a concept that is often overlooked is inextricably linked to the matter of employee engagement. Businesses that provide superior customer service tend to have very motivated employees who are aware of their contribution to the overall service delivery process. When people go to work knowing that their employer is willing to provide for their needs as well as empower them to enhance the quality of service delivery to the customers, it only makes business sense that these people would do everything within their powers to ensure that the outcome of every transaction is satisfactory to the customer.
As businesses grow, delivering a consistent and high-quality customer experience becomes increasingly complex. What works well for a small customer base often becomes difficult to maintain at scale. Expanding into new markets, adding digital channels, and serving a wider demographic bring unique challenges that demand careful strategy and execution.
One of the most significant challenges in scaling customer experience is maintaining consistency across multiple touchpoints while managing operational complexity. Customers expect the same level of service whether they interact with a brand through a mobile app, website, physical store, or call center.
The key to overcoming these challenges lies in building centralized systems, strong governance, and employee training programs that align all teams with the same customer-first philosophy. Consistency is achieved not through rigid uniformity, but by empowering teams with the right tools and data to deliver personalized yet predictable experiences at every interaction.
Technology is essential for enabling customer experience in business today, especially in the digital environment. Ranging from simple AI automated chatbots to complex CRM systems, organizations now have alternatives that can significantly improve their customer engagement level. But the bottom line is not in the adoption of technology solutions but in the adoption of technology solutions in line with certain strategic aims concerning customer needs and problems. Customer experience should not be a reason to adopt technology, but it should be a reason to avoid it.
Customers are set to become even more significant in the future than they have been in the past. Opportunities are coming from the technologies and resultant shifts in the customers’ characteristics on how the experience could be optimized. Only those organizations that are aware of such trends and, at the same time, are customer-oriented will be in a better place to reap big in the end. The kind of specialized companies that remain on this country's playing field are the ones that can manage to deal with such unpredictable changes in experiences while at the same time seeking to fine-tune their uniquely personal touch.
Artificial Intelligence and automation are reshaping the way businesses deliver customer experience. From predictive recommendations to instant query resolution, these technologies enable brands to serve customers faster, smarter, and at scale.
When balanced effectively, AI and automation transform CX from reactive to proactive, delivering both speed and personalization without losing the human touch.
While technology unlocks powerful new ways to enhance CX, it also raises concerns around trust and privacy. In the digital era, customers are increasingly aware of how their data is collected and used, and they expect brands to safeguard it responsibly.
In the end, trust is the foundation of customer experience. No matter how advanced AI and automation become, they must operate within a framework that respects privacy and ensures safe, transparent digital experiences.
To any organization with a mission to achieve business success Customer Focus Initiatives, the practice of Customer Experience Management, and continuous assessment and improvement form the core strategy. This is customer feedback, which involves collecting data from the customers, measuring organizational performance, and making relevant changes based on the data collected. The leading organizations know that customer experience is not an isolated event but a highly important, continuous process of development and improvement.
Measuring customer experience requires clear and reliable metrics. Without them, businesses cannot track progress, identify gaps, or prove the impact of their CX initiatives. Three of the most widely used Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide a strong foundation:
Together, these metrics help businesses quantify how customers feel, how they behave, and whether CX strategies are truly working.
While tracking CX metrics is valuable, their real power comes from connecting them to broader business results. Customer experience doesn’t exist in isolation—it directly influences revenue, growth, and brand equity.
By consistently linking customer experience metrics to financial and operational outcomes, businesses strengthen the case for continued CX investments. This not only helps win leadership buy-in but also ensures that customer experience remains central to long-term business strategy.
As more and more product and service offerings move closer to a basic replacement for each other, the importance of customer experience becomes the key competitive advantage. Effective experience producers build virtually unassailable competitive moats into their operations. This is because unlike products that may be imitated and prices that can be matched to those of competitors, the intricate network of relationships that build end-customer experiences is not easily imitated.

Customer experience is, therefore, a crucial factor in the lean of contemporary business organizations. Customer experience is one of the critical success factors in business, and every company that tries to pay adequate attention to this factor as well as dedicate enough efforts to enhance the level of customer experience enjoyed in their facilities shall be well poised for long-term success in business. Approximately, as markets develop and customers become more demanding, sustaining a solid business success, customer orientation simply becomes more important. The enterprises that adjust to this and ensure they allocate the required capital will likely be prepared for a world of a more progressively competitive business environment.