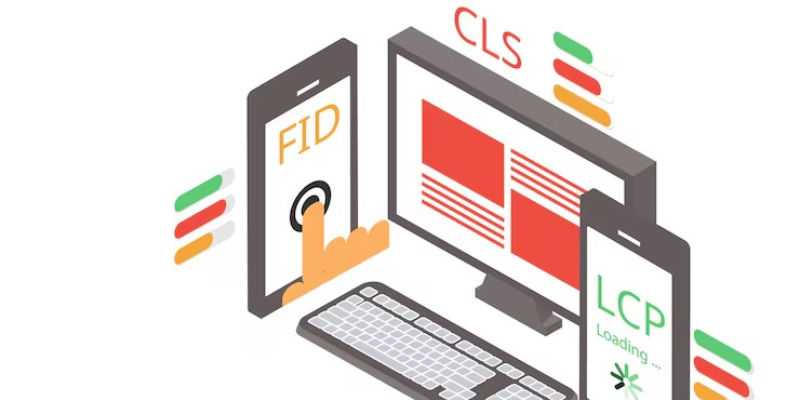


Core Web Vitals are metrics that Google created to measure the user experience (UX) of websites. They emphasize three specific web performance aspects that directly impact user experience: loading, interactivity, and visual stability. Here is a detailed analysis of each one of Google's Core Web Vitals:
LCP is the amount of time it takes for a webpage's largest visually perceivable element, which could be an image, video, or text block, to completely load.
In the case of LCP with a fast load, users are likely to believe the page is loading faster where content is the core load and if LCP takes long, the users perceive a page as slow and even unresponsive. It is to have an LCP below 2.5 seconds, an LCP between 2.5 to 4 seconds needs to be improved, and more than 4 seconds is bad. Resizing or compressing images and videos is possible using new formats such as WebP.
Server response time has improved (for example, through better hosting or CDN). Fewer, if any, render-blocking resources like CSS and JavaScript content.
FID calculates the amount of time that has passed from the beginning of a user interaction with any element such as clicking on the link or touching the website button until the user’s browser responds after said interaction.
Users frustrated by these protracted delays may simply navigate away from a site. A good FID is where it's less than 100 milliseconds. From 100 to 300 milliseconds must improve, and more than 300 milliseconds is bad.
CLS is the measure of page visual stability. It quantifies how much visible content shifts upon loading. This metric therefore considers all unexpected layout shifts that happen as the page loads.
A high CLS is frustrating because it means stuff is moving around on the screen, which may cause accidents in clicking the wrong items or losing their place on the page. A good CLS is 0.1 or less than that. Anything between 0.1 and 0.25 is needed to improve, and any score that's more than 0.25 is poor.
Improvement Strategies: The size attributes must be placed in images and videos to always pre-load some space. Avoid placing new content above current content without proper placeholder usage. Ensure fonts load accurately and avoid text shifting up.
Avoid Core Web Vitals errors to improve user experience on your website. These are some of the common Core Web Vitals mistakes to avoid:
Slow server response could make large visible content elements display after a considerable amount of time.
Render-blocking CSS or JavaScript files could make the content element load relatively slow.
Large images that are not compressed or not size-corrected can take a long time for your pages to load.
Scripts that take longer to load and execute are likely to block user interactions, hence, they will be delayed.
Ads, widgets, and tracking scripts introduce heavy loads and thus delay their execution, thereby impacting the interactivity.
The primary thread cannot respond to interactions since it is busy processing its tasks.
If an image is not set to define size, then the layout shifts because it loads.
The unoptimized font being loaded can make text shift as the correct one would be applied.

Google's Core Web Vitals improve the overall user experience. Users are likely to be happy and stay longer with good core web vitals.
Even in the ranking algorithm, Google has included core web vitals. Websites that rank higher on these metrics may get higher visibility on search engine result pages.
Better UX will lead to a higher conversion rate because people are likely to interact and make transactions on a fast, stable site.
Google PageSpeed Insights not only gives much more detail about performance but also includes recommendations for improvement.
Lighthouse is an open-source audit tool of web performance concerning Core Web Vitals, a Chrome Extension that provides real-time feedback to you for any page where you may be browsing.
Search Console shows how far your website performed against the Core Web Vitals of user experience.
Google's core web vitals enhance the user experience of websites since it makes the whole experience entertaining. One can be satisfied when their needs are met in less amount of time.
A good experience will bring users back. Users who are engaged are likely to explore more pages, sign up for services, or make purchases.
With a smooth responsive, and visually stable experience, users have better chances of performing desired actions that result in higher conversion rates.
Google has the best possible results for the users since it favors pages that have a good user experience. Core Web Vitals measure several facets of loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability that are important for a good user experience.
Pages that respond to user inputs, render quickly and have visual stability engage users more and help retain them on the website. More engagement by the users is a signal of a page's value for Google.
The Core Web Vitals are integrated into Google's Page Experience update, published in 2021. This update added Core Web Vitals as a ranking signal and other factors including mobile-friendliness, safe browsing, and HTTPS security.
Sites scoring above or at the thresholds for LCP, FID, and CLS will likely rank better than those failing to achieve those standards.
With mobile device browsing taking more of the online experience, Google is focusing on mobile device-friendly experiences. Core Web Vitals particularly speaks to that because it talks about fast loading and good interaction for the mobile device user.
Sites performing well under the Core Web Vitals metric are likely to rank better in mobile devices search giving more weight to mobile user experience.
Google scans the web constantly for the level of performance of your website. As they keep seeking a better knowledge of how the user is evolving, they create new and diverse metrics for ranking factors and change various thresholds that are linked to the respective metrics. You remain aligned with all the novel benchmarks established by Google over time as you stay updated with the above-mentioned Core Web Vitals.
Even after the update of the Google algorithm, the requirement of user experiences will remain the same along with the modification in the ranking core web vital.
PageSpeed is an excellent way of improving Google's Core Web Vitals, the metrics Google uses to measure user experience on websites. Here's how PageSpeed affects these metrics:
PageSpeed can reduce the time it takes to load the largest element on the page. Techniques such as image optimization, lazy loading, and minifying CSS/JavaScript can significantly improve LCP.
Fast page loading times reduce the waiting time before users can interact with a page. PageSpeed minimizes render-blocking resources and optimizes scripts to reduce FID, thus ensuring a smooth user experience.
A page doesn't shift during loading for the better CLS. The best practice in PageSpeed is that of setting image size attributes using CSS for layout and ensuring predictability when loading an element.
Websites are an important asset for brands. It is the place where almost all transactions take place. By ensuring that you provide a good user experience and an easy-to-navigate website, the website's ranking can be improved. Bud is an expert SEO agency in Bangalore. We can help optimize your website's UX to get maximum traffic on your website with the help of our SEO specialists.